- Home
- Departments
- Urology
Urology
Urology is a branch of medicine that focuses on medical conditions of the male and female urinary tract systems. The urologist is a medical professional that specialises in the urinary system in both men and women. In ancient times, doctors used to examine the urine of a patient for clues about their illness.
Overview
Urology is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of conditions affecting the urinary tract and the male reproductive system. Urologists are medical doctors who specialize in urology and have expertise in both surgical and non-surgical treatment options for urological conditions.
The urinary tract includes organs such as the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, which are responsible for the production, storage, and elimination of urine. The male reproductive system includes the testes, prostate gland, penis, and associated structures.
Urologists diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions, including:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Kidney stones
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Prostate cancer
- Bladder cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Urinary incontinence
- Erectile dysfunction
- Male infertility
- Overactive bladder
- Interstitial cystitis
- Urethral strictures
- Urinary tract obstructions
- Pelvic organ prolapse
- Male and female voiding dysfunctions
Urologists utilize various diagnostic techniques such as physical examinations, imaging studies (such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI), urine and blood tests, and specialized procedures (cystoscopy, urodynamic studies) to evaluate and diagnose urological conditions.
Treatment options in urology can range from medication and lifestyle modifications to surgical interventions, depending on the specific condition and its severity. Urologists may perform surgeries such as transurethral resection, laser procedures, prostatectomy, nephrectomy, or reconstructive surgeries.
Urology encompasses a broad range of urological conditions and requires comprehensive knowledge of both medical and surgical approaches. Urologists often collaborate with other specialists, such as oncologists, radiologists, and nephrologists, to provide multidisciplinary care for their patients. Regular check-ups with a urologist are important for the early detection and management of urological conditions.
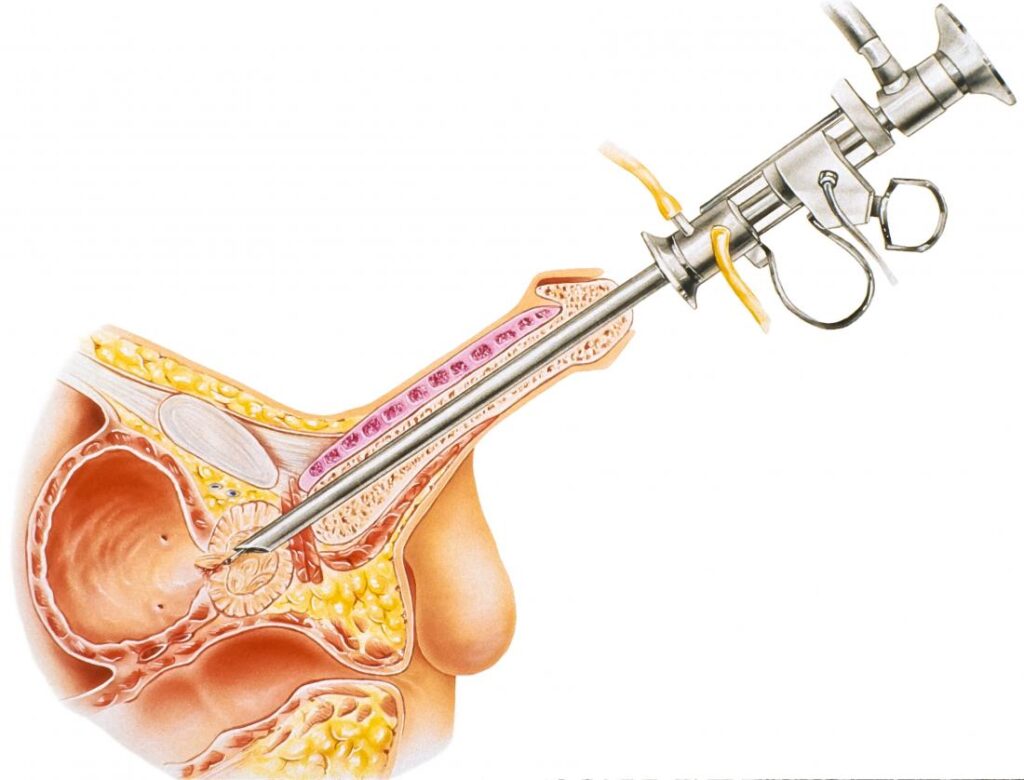
TURP
TURP (Transurethral Resection of the Prostate) and TURIS (Transurethral Resection in Saline) are both surgical procedures used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition characterized by the enlargement of the prostate gland.
TURP is a well-established surgical technique that has been used for many years. During TURP, a special instrument called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra into the prostate gland. The resectoscope has a wire loop or electrode that is used to remove excess prostate tissue by cutting or vaporizing it. This procedure helps to relieve urinary obstruction and improve urine flow.
On the other hand, TURIS is a newer variation of the traditional TURP procedure. TURIS involves using a saline solution instead of traditional irrigation fluid (glycine or sorbitol) during the resection of the prostate tissue. The use of saline as an irrigation fluid aims to reduce the absorption of fluids into the bloodstream and minimize the potential complications associated with fluid absorption, such as dilutional hyponatremia.
The principles and techniques of TURIS are similar to TURP, with the main difference being the type of irrigation fluid used. The use of saline during TURIS helps maintain electrolyte balance during the procedure and reduces the risk of complications related to fluid overload.
Both TURP and TURIS are effective procedures for relieving urinary symptoms caused by BPH. The choice between the two techniques may depend on the surgeon’s preference, the patient’s specific condition, and the availability of equipment and resources in the medical facility. It is important to consult with a urologist to determine the most appropriate treatment approach for an individual case.
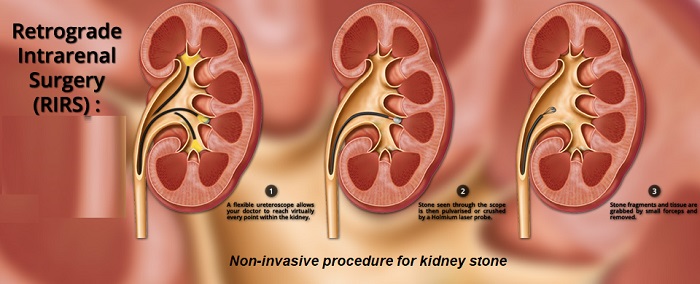
RIRS
Retrograde Intra-Renal Surgery (RIRS) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to treat kidney stones or other conditions within the kidney. It is also known as Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery.
In RIRS, a thin flexible tube called a ureteroscope is inserted through the urethra and passed through the bladder and up into the ureter until it reaches the kidney. The ureteroscope has a camera and surgical instruments attached to it, allowing the surgeon to visualize the inside of the kidney and perform various procedures.
Once the ureteroscope is in place, the surgeon can use laser energy or other specialized instruments to break up or remove the kidney stones or perform other necessary treatments. The fragmented stones can then be extracted or allowed to pass out naturally through urine.
RIRS is a preferred option for patients with smaller kidney stones or those located in hard-to-reach areas within the kidney. It offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including reduced risk, shorter recovery time, and minimal scarring.
It is important to note that the specific details of the procedure can vary depending on the individual case and the surgeon’s approach. The decision to perform RIRS is made after a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition and imaging studies, and it is typically performed under general anesthesia.
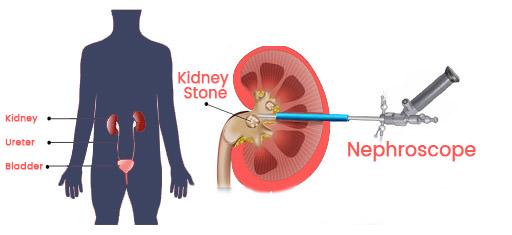
PCNL
Endourology is a subspecialty within urology that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of urological conditions using minimally invasive techniques. It involves using endoscopes and other specialized instruments to access and treat the urinary tract and related structures.
The term “endourology” is derived from two components: “endo” meaning “within” or “inside” and “urology” referring to the medical field specializing in the urinary system. Endourological procedures are typically performed using natural body openings or small incisions, resulting in reduced trauma, faster recovery, and minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgeries.
Some common endourological procedures include:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): It is a surgical procedure to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by removing excess prostate tissue through the urethra.
- Ureteroscopy: This procedure involves the use of a thin, flexible tube called a ureteroscope to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the ureters, such as kidney stones, strictures, or tumors.
- Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL): It is a procedure used to remove large kidney stones through a small incision in the back. A nephroscope is inserted through the incision to access and remove the stones.
- Laser Lithotripsy: This technique utilizes laser energy to break down kidney or ureteral stones into smaller fragments, which can be easily passed through the urinary system or removed with specialized tools.
- Endoscopic Removal of Bladder Tumors: Endourological techniques can be employed to diagnose and treat bladder tumors by removing them through the urethra using a cystoscope.
Endourology has revolutionized the field of urology by providing less invasive alternatives to traditional open surgeries. It offers numerous benefits, including shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, reduced complications, and improved patient outcomes. Endourological procedures are typically performed by urologists who have specialized training and expertise in minimally invasive techniques.
Emergency Cases
Please feel welcome to contact our friendly reception staff with any general or medical enquiry call us.

